Theories
The main theories that explain personality and how it can influence sports performance are:
- Martens Schematic View
- The Psychodynamic Theory
- Trait Theory
- Situational Approach
- Interactional Approach
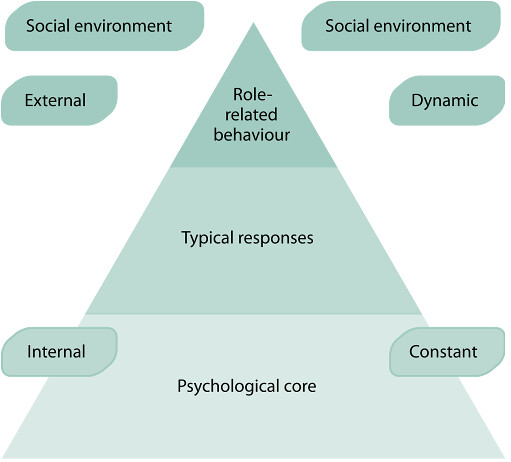
In this view personality is seen as having three different levels that are related to each other, these personality views are:
- Psychological core
- Typical responses
- Role-related behavior
Typical responses are the way that you respond to the world around you and with different situations you find yourself in will find yourself responding differently. For example if you get fouled in football you may shout and make a fuss but then if you are meeting new people you may be quiet and shy because you don't want to overwhelm them or come across the wrong way so you change the way you are around people because your environment has changed. These are often good indicators of your psychological core.
Role related behavior is often the circumstances you find yourself in and this is the most changeable aspect of personality. Your personality changes as your perception of your environment changes. For example you might be the captain of your football team at college and showing leader roles and giving out instructions then working at your part time job and following instructions you are being given, you are changing how you deal with this because your environment has change from the football pitch to the work place.
Psychodynamic theory
This approach to personality says that it is made up of two parts which is conscious and unconscious parts. The first part is called the 'id' which stands for instinctive drive. This is the part of your personalty that does things unconsciously and you do things without even thinking about them. The second part of your personality is your ego, your ego is conscious. You also have a super ego which is your moral conscience. The effect of the ego and super ego are seen in football when a penalty needs to be taken but a player refuse to take one with the fear he/she might let their team down. What most people don't realize that not all behavior is under the conscious control of the athletes.
Trait theory
Trait theories suggest that individuals have certain characteristics that will partly determine how they behave. Traits are mainly inherited and the two main ones are:
- An introversion-extroversion dimension.
- A stable-neurotic dimension.
Are individuals who don't actively seek excitement and would rather be in a calm environment They tend to prefer tasks that require concentration and dislike the unexpected.
Extroverts
Tend to become bored quickly, are poor at tasks that require a lot of concentration and constantly seek change and excitement. Extroverts are said to be less responsive to pain. Extroverts are be more successful in sporting situations than introverts.
Stable individuals
Are people who tend to be more easy-going and even tempered. Neurotic (unstable) people tend to be more restless, excitable, have a tendency to become anxious and are more highly aroused.
Situational approach
The situation approach is different from the trait theories approach as it says that behaviors dependent on your situation and the environment you are in. This situation argues that it is more important than traits.
There is research that supports the fact that in sporting behaviors an individuals may be introverted displaying characteristics such as tolerance and shyness but also may take part in a sport that requires them to be more extroverted and display aggression in sporting situations.
Interactional approach
To predict behavior in a sporting situation, you need to consider how the situation and personality traits link and work together. This is known as the interactional approach to personality and sport behavior.
The interactional approach is the view widely accepted by sports psychologists when explaining behavior. This theory suggests that when situational factors are particularly strong, for example during a competitive sporting situation like a penalty shoot out in football, they are more likely to predict behavior than personality traits. The athlete who tends to be quiet and shy in an everyday situation is likely to run towards an ecstatic crowd screaming if he crowd screaming if he scores the winning penalty.